Angular 2 is a framework to help us build client applications in HTML and
either JavaScript or a language (like Dart or TypeScript) that compiles to JavaScript.
Angular 2 for Dart is published as the angular2 package, which
(like many other Dart packages) is available via the Pub tool.
With Angular, we write applications by composing HTML templates with Angularized markup, writing component classes to manage those templates, adding application logic in services, and handing the top root component to Angular's bootstrapper.
Angular takes over, presenting our application content in a browser and responding to user interactions according to the instructions we provided.
Of course there is more to it than this. We're cruising at high altitude in this overview. We're looking for landmarks. We should expect the object below to be fuzzy and obscured by occasional clouds. Details become more clear and precise when we land in the chapters themselves.
An Angular 2 for Dart application rests on seven main building blocks:
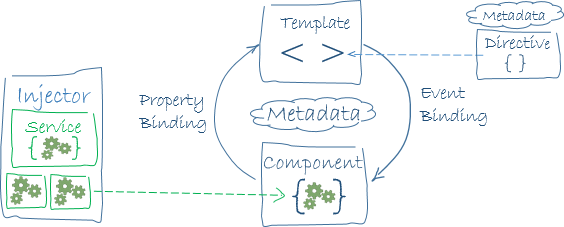
Learn these seven and we're on our way.
Components
A component controls a patch of screen real estate that we could call a view. A set of navigation links, a list of heroes, a hero editor ... they're all views controlled by components.
We define a component's application logic — what it does to support the view — inside a class. The class interacts with the view through an API of properties and methods.
A HeroListComponent, for example, might have a heroes property that returns an array of heroes
that it acquired from a service.
It might have a selectHero() method that sets a selectedHero property when the user clicks to choose a hero from that list.
The component might be a class like this:
Angular creates, updates, and destroys components as the user moves through the application. The developer can take action at each moment in this lifecycle through optional lifecycle hooks.
We may wonder who is calling the component's constructor? Who provides the service parameter?
For the moment, have faith that Angular will call the constructor and deliver an
appropriate HeroService when we need it.
Templates
We define a component's view with its companion template. A template is a form of HTML that tells Angular how to render the component.
A template looks like regular HTML much of the time ... and then it gets a bit strange. Here is a
template for our HeroListComponent:
This template features typical HTML elements like <h2> and <div>.
But what are *ngFor, {{hero.name}}, (click), [hero], and <hero-detail>?
They're examples of Angular's template syntax.
We'll grow accustomed to that syntax and may even learn to love it.
Take a look at the last line,
which has the <hero-detail> tag.
That tag adds a custom element representing a component we haven't seen yet,
a HeroDetailComponent.
The HeroDetailComponent is a different component than the HeroListComponent we've seen.
The HeroDetailComponent (code not shown) presents facts about a particular hero, the
hero that the user selects from the list presented by the the HeroListComponent.
The HeroDetailComponent is a child of the HeroListComponent.
Notice how <hero-detail> rests comfortably among native HTML elements.
We can and will mix our custom components with native HTML in the same layouts.
In this manner we'll compose complex component trees to build out our richly featured application.
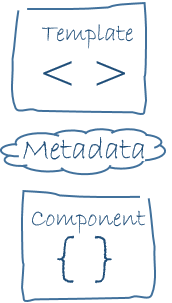
Metadata

Metadata tells Angular how to process a class.
Looking back at the code for HeroListComponent, we see that it's just a class.
There is no evidence of a framework, no "Angular" in it at all.
In fact, it really is just a class. It's not a component until we tell Angular about it.
We tell Angular that HeroListComponent is a component by attaching metadata to the class.
In Dart, we attach metadata by using an annotation.
Here's some metadata for HeroListComponent:
Here we see the @Component annotation, which (no surprise) identifies the class
immediately below it as a component class.
Annotations often have configuration parameters.
The @Component annotation takes parameters to provide the
information Angular needs to create and present the component and its view.
Here we see a few of the possible @Component parameters:
selector: A CSS selector that tells Angular to create and insert an instance of this component where it finds a<hero-list>tag in parent HTML. For example, if an app's HTML contains<hero-list></hero-list>, then Angular inserts an instance of theHeroListComponentview between those tags.templateUrl: The address of this component's template, which we showed above.directives: An array of the components or directives that this template requires. We saw in the last line of our template that we expect Angular to insert aHeroDetailComponentin the space indicated by<hero-detail>tags. Angular will do so only if we mention theHeroDetailComponentin thisdirectivesarray.providers: An array of dependency injection providers for services that the component requires. This is one way to tell Angular that our component's constructor requires aHeroServiceso it can get the list of heroes to display. We'll get to dependency injection later.
At runtime, Angular discovers the metadata specified by the @Component
annotation. That's how Angular learns how to do "the right thing".
The template, metadata, and component together describe the view.
We apply other metadata annotations in a similar fashion to guide Angular behavior.
@Injectable, @Input, @Output, and @RouterConfig are a few of the more popular annotations
we'll master as our Angular knowledge grows.
The architectural takeaway is that we must add metadata to our code so that Angular knows what to do.
Data binding
Without a framework, we would be responsible for pushing data values into the HTML controls and turning user responses into actions and value updates. Writing such push/pull logic by hand is tedious, error-prone, and a nightmare to read as any experienced jQuery programmer can attest.
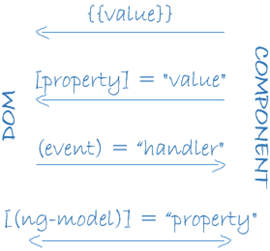
Angular supports data binding, a mechanism for coordinating parts of a template with parts of a component. We add binding markup to the template HTML to tell Angular how to connect both sides.
There are four forms of data binding syntax. Each form has a direction — to the DOM, from the DOM, or in both directions — as indicated by the arrows in the diagram.
We saw three forms of data binding in our example template:
The
{{hero.name}}interpolation displays the component'shero.nameproperty value within the<div>tags.The
[hero]property binding passes the value ofselectedHerofrom the parentHeroListComponentto theheroproperty of the childHeroDetailComponent.The
(click)event binding calls the component'sselectHeromethod when the user clicks a hero's name.
Two-way data binding is an important fourth form
that combines property and event binding in a single notation, using the ngModel directive.
We didn't have a two-way binding in the HeroListComponent template;
here's an example from the HeroDetailComponent template:
In two-way binding, a data property value flows to the input box from the component as with property binding. The user's changes also flow back to the component, resetting the property to the latest value, as with event binding.
Angular processes all data bindings once per JavaScript event cycle, depth-first from the root of the application component tree.
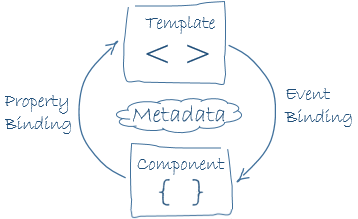
We don't know all the details yet, but it's clear from these examples that data binding plays an important role in communication between a template and its component.
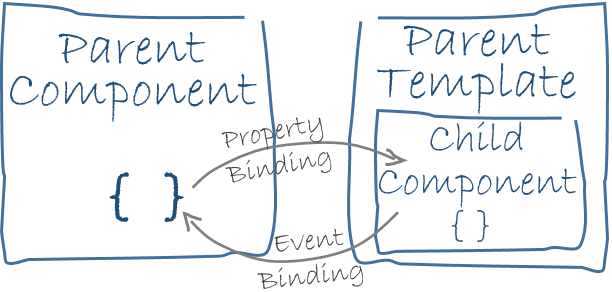
Data binding is also important for communication between parent and child components.
Directives
Angular templates are dynamic. When Angular renders them, it transforms the DOM according to the instructions given by directives.
A directive is a class with directive metadata. In Dart we apply the @Directive annotation
to attach metadata to the class.
We already met one form of directive: the component. A component is a directive-with-a-template;
a @Component annotation is actually a @Directive annotation extended with template-oriented features.
While a component is technically a directive, components are so distinctive and central to Angular applications that we chose to separate components from directives in this architectural overview.
Two other kinds of directives exist: structural and attribute directives.
They tend to appear within an element tag like attributes, sometimes by name but more often as the target of an assignment or a binding.
Structural directives alter layout by adding, removing, and replacing elements in DOM.
Our example template uses two built-in structural directives:
*ngFortells Angular to stamp out one<div>per hero in theheroeslist.*ngIfincludes theHeroDetailcomponent only if a selected hero exists.
In Dart, the only value that is true is the boolean value true; all
other values are false. JavaScript and TypeScript, in contrast, treat values
such as 1 and most non-null objects as true. For this reason, the JavaScript
and TypeScript versions of this app can use just selectedHero as the value
of the *ngIf expression. The Dart version must use a boolean operator such
as != instead.
Attribute directives alter the appearance or behavior of an existing element. In templates they look like regular HTML attributes, hence the name.
The ngModel directive, which implements two-way data binding, is
an example of an attribute directive. ngModel modifies the behavior of
an existing element (typically an <input>)
by setting its display value property and responding to change events.
Angular ships with a small number of other directives that either alter the layout structure
(for example, ngSwitch)
or modify aspects of DOM elements and components
(for example, ngStyle and ngClass).
Of course, we can also write our own directives. Components such as
HeroListComponent are one kind of custom directive.
Services

Services is a broad category encompassing any value, function, or feature that our application needs.
Almost anything can be a service. A service is typically a class with a narrow, well-defined purpose. It should do something specific and do it well.
Examples include:
- logging service
- data service
- message bus
- tax calculator
- application configuration
There is nothing specifically Angular about services. Angular itself has no definition of a service. There is no service base class, and no place to register a service.
Yet services are fundamental to any Angular application. Our components are big consumers of services.
We prefer our component classes lean. Our components don't fetch data from the server, they don't validate user input, and they don't log directly to console. They delegate such tasks to services.
A component's job is to enable the user experience and nothing more. It mediates between the view (rendered by the template) and the application logic (which often includes some notion of a model). A good component presents properties and methods for data binding. It delegates everything nontrivial to services.
Angular doesn't enforce these principles. It won't complain if we write a "kitchen sink" component with 3000 lines.
Angular does help us follow these principles by making it easy to factor our application logic into services and make those services available to components through dependency injection.
Dependency injection
Dependency injection is a way to supply a new instance of a class with the fully-formed dependencies it requires. Most dependencies are services. Angular uses dependency injection to provide new components with the services they need.
Angular can tell which services a component needs by looking at the types of its constructor parameters.
For example, the constructor of our HeroListComponent needs a HeroService:
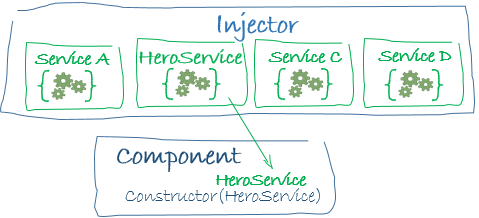
When Angular creates a component, it first asks an injector for the services that the component requires.
An injector maintains a container of service instances that it has previously created. If a requested service instance is not in the container, the injector makes one and adds it to the container before returning the service to Angular. When all requested services have been resolved and returned, Angular can call the component's constructor with those services as arguments. This is what we mean by dependency injection.
The process of HeroService injection looks a bit like this:
If the injector doesn't have a HeroService, how does it know how to make one?
In brief, we must have previously registered a provider of the HeroService with the injector.
A provider is something that can create or return a service, typically the service class itself.
We can register providers at any level of the application component tree. We often do so at the root when we bootstrap the application so that the same instance of a service is available everywhere.
Alternatively, we might register at a component level:
Registering at a component level means we get a new instance of the service with each new instance of that component.
Points to remember about dependency injection:
Dependency injection is wired into the Angular framework and used everywhere.
The injector is the main mechanism.
- An injector maintains a container of service instances that it created.
- An injector can create a new service instance from a provider.
A provider is a recipe for creating a service.
We register providers with injectors.
Other stuff
We've learned just a bit about the seven main building blocks of an Angular application:
That's a foundation for everything else in an Angular application, and it's more than enough to get going. But it doesn't include everything we'll need or want to know.
Here is a brief, alphabetical list of other important Angular features and services. Most of them are covered in this Developers Guide (or soon will be).
Animations: A forthcoming animation library makes it easy for developers to animate component behavior without deep knowledge of animation techniques or CSS.
Bootstrap: A method to configure and launch the root application component.
Change detection: Learn how Angular decides that a component property value has changed and when to update the screen. Learn how it uses zones to intercept asynchronous activity and run its change detection strategies.
Component router: With the component Router service, users can navigate a multi-screen application in a familiar web browsing style using URLs.
Events: The DOM raises events. So can components and services. Angular offers mechanisms for publishing and subscribing to events including an implementation of the RxJS Observable proposal.
Forms: Support complex data entry scenarios with HTML-based validation and dirty checking.
HTTP: Communicate with a server to get data, save data, and invoke server-side actions with this Angular HTTP client.
Lifecycle hooks: We can tap into key moments in the lifetime of a component, from its creation to its destruction, by implementing the lifecycle hook interfaces.
Pipes: Services that transform values for display. We can put pipes in our templates to improve the user experience. Consider this
currencypipe expression:
It displays a price of "42.33" as
$42.33.Testing: Angular provides a testing library to run unit tests on our application parts as they interact with the Angular framework.